Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
An internal combustion engine is engineered to provide optimal performance, fuel economy and emissions when running within a specific temperature range. For this reason, every vehicle is equipped with a cooling system that relies on an engine coolant temperature sensor to keep the engine running at its best.
A faulty engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor may lead to engine overheating and lots of other troubles related to the engine. Let’s check the signs of a bad ECT sensor to prevent such problems in your vehicle.
Your check engine lights is on
If your engine control module does not receive signals from your ECT sensor, or they’re incorrect, it will make the check engine light come on.
The engine stalls or hesitates
A cold engine needs more fuel to start and run. A faulty sensor may confuse the engine control module, providing incorrect temperature readings, so the computer will not send a signal to the fuel system to add extra gas to the fuel/air mixture. That’s why your engine may stall or hesitate.
Poor fuel economy
From the start of the engine and until it’s warmed up, the engine control module relies on the ECT sensor for fuel control. As soon as the engine reaches its normal operating temperature, the computer will switch to the data received from the oxygen sensor for more accurate readings. However, if the coolant sensor is faulty and feeds the module with incorrect information, the change may not happen, keeping the engine consuming more fuel than it needs.
Lack of performance
As it was mentioned above, a faulty ECT sensor may affect fuel consumption and other engine systems, and, therefore, cause misfiring due to excessive fuel in the combustion chamber or incorrect ignition timing.
Overheating
The engine’s cooling system is operated by the engine control module that relies on the coolant sensor’s readings. If they are wrong, the module will not turn on the cooling fan, which will cause engine overheating. If so, you should stop the car and shut down the engine.
How the ECT sensor works
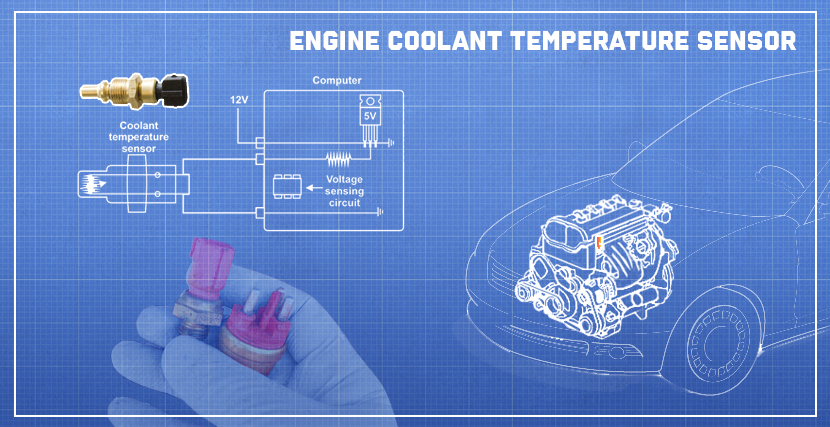
The job of an engine coolant temperature sensor, often called a coolant sensor, is to measure the engine’s temperature and to supply these data to the control unit. Its proper operation is crucial for efficient fuel delivery and ignition timing as well as engine performance.
The sensor can be found in the engine block or cylinder head where the coolant is the hottest. Some vehicles may feature several ECT sensors for the most accurate temperature reading.
One side of the sensor that goes inside the engine is always submerged in coolant. The hotter the coolant is, the higher voltage is sent to the engine control module that calculates the temperature based on the voltage received.
On some older vehicles, the coolant temperature sensor may supply readings directly to the temperature gauge on the dashboard.
How to fix a faulty ECT sensor
It’s always a good idea to inspect the system before replacing the sensor. A qualified technician can do this with a scan tool or digital multimeter.
Please be advised that the sensor will not function correctly if it is not fully submerged in coolant. You should check the coolant level before replacing the sensor.
A faulty sensor is not repairable and must be replaced. If there are any contaminants on its tip, you should consider having the cooling system flushed.
On most vehicles, the sensor is easy to access. However, you should hire a professional to have the job done to prevent any damage to the engine.